Low lamin A levels enhance confined cell migration and metastatic capacity in breast cancer | bioRxiv

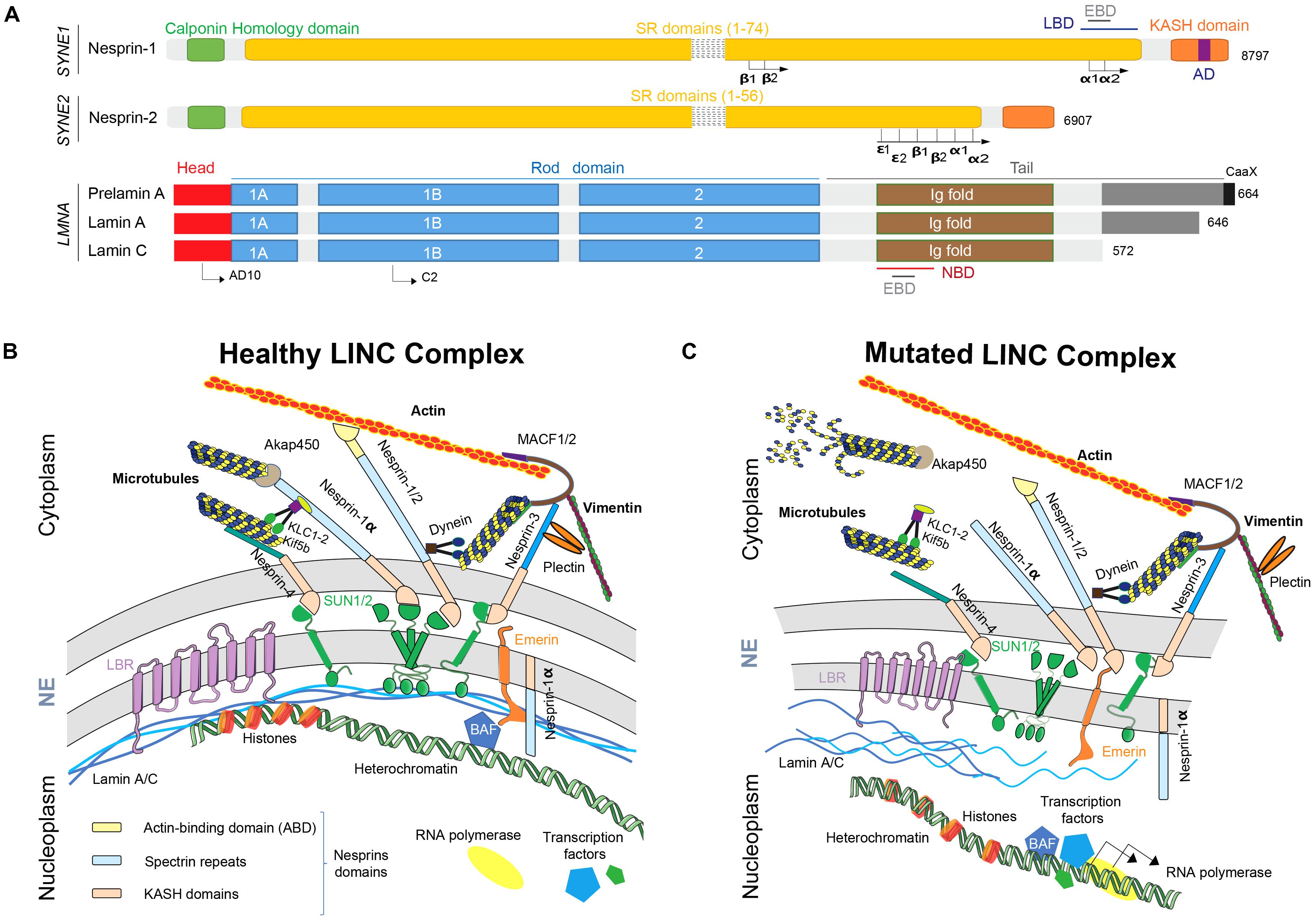
Mutant lamins cause nuclear envelope rupture and DNA damage in skeletal muscle cells | Nature Materials
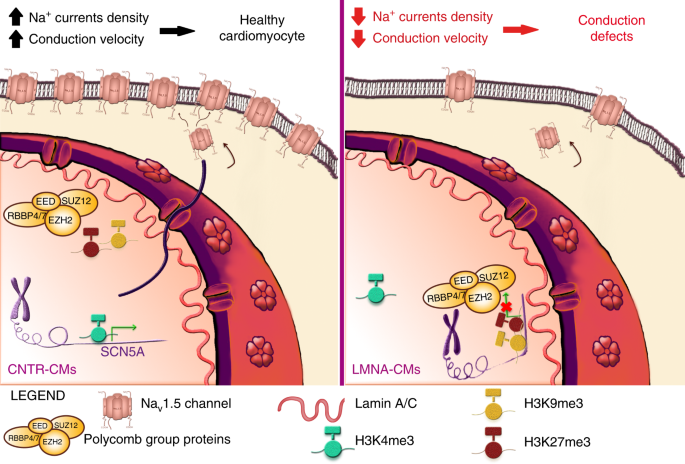
The K219T-Lamin mutation induces conduction defects through epigenetic inhibition of SCN5A in human cardiac laminopathy | Nature Communications

Analysis of lamins expression patterns and localization in Drosophila... | Download Scientific Diagram

Lamin B1-GFP ( a ± c ) and lamin C-GFP fluorescence ( d ) combined with... | Download Scientific Diagram
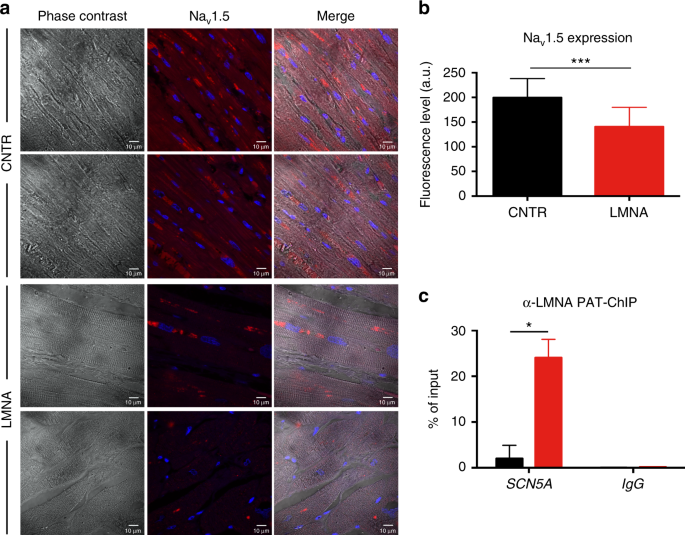
The K219T-Lamin mutation induces conduction defects through epigenetic inhibition of SCN5A in human cardiac laminopathy | Nature Communications

Mutant lamins cause nuclear envelope rupture and DNA damage in skeletal muscle cells | Nature Materials

Reduced nuclear lamin A/C enhances cancer cell squeezing through rigid barriers, does not facilitate endothelial crossing, and impairs experimental metastasis | bioRxiv

Mutant lamins cause nuclear envelope rupture and DNA damage in skeletal muscle cells | Nature Materials

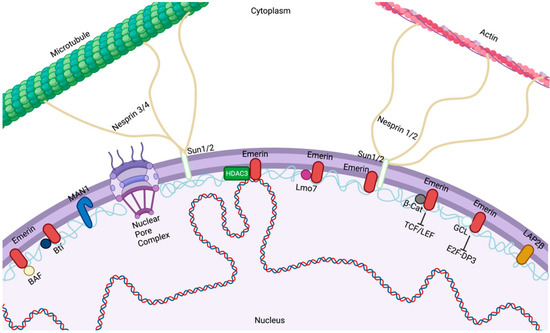
The ESCRT machinery counteracts Nesprin-2G-mediated mechanical forces during nuclear envelope repair - ScienceDirect
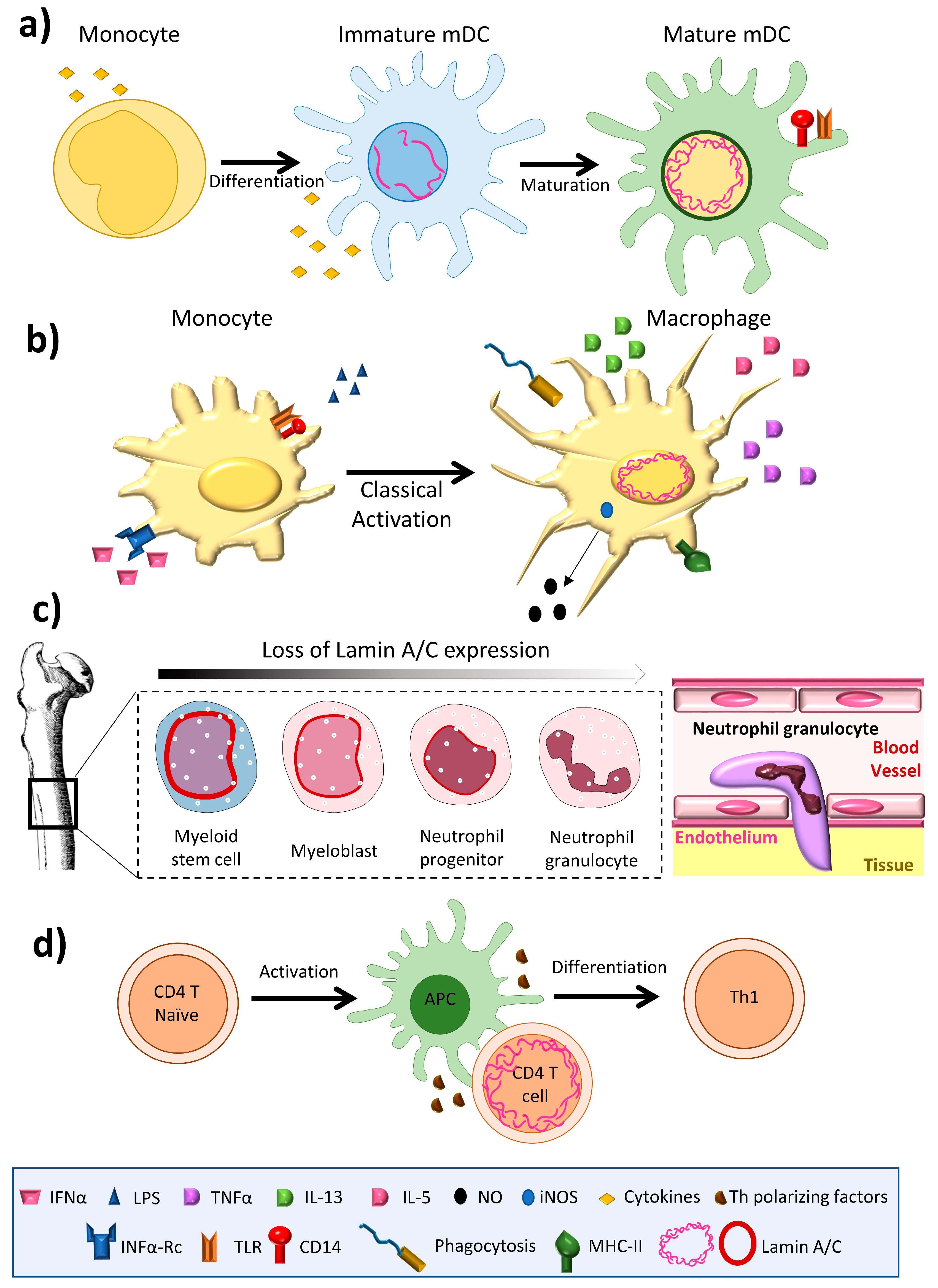
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Lamin A/C and the Immune System: One Intermediate Filament, Many Faces | HTML
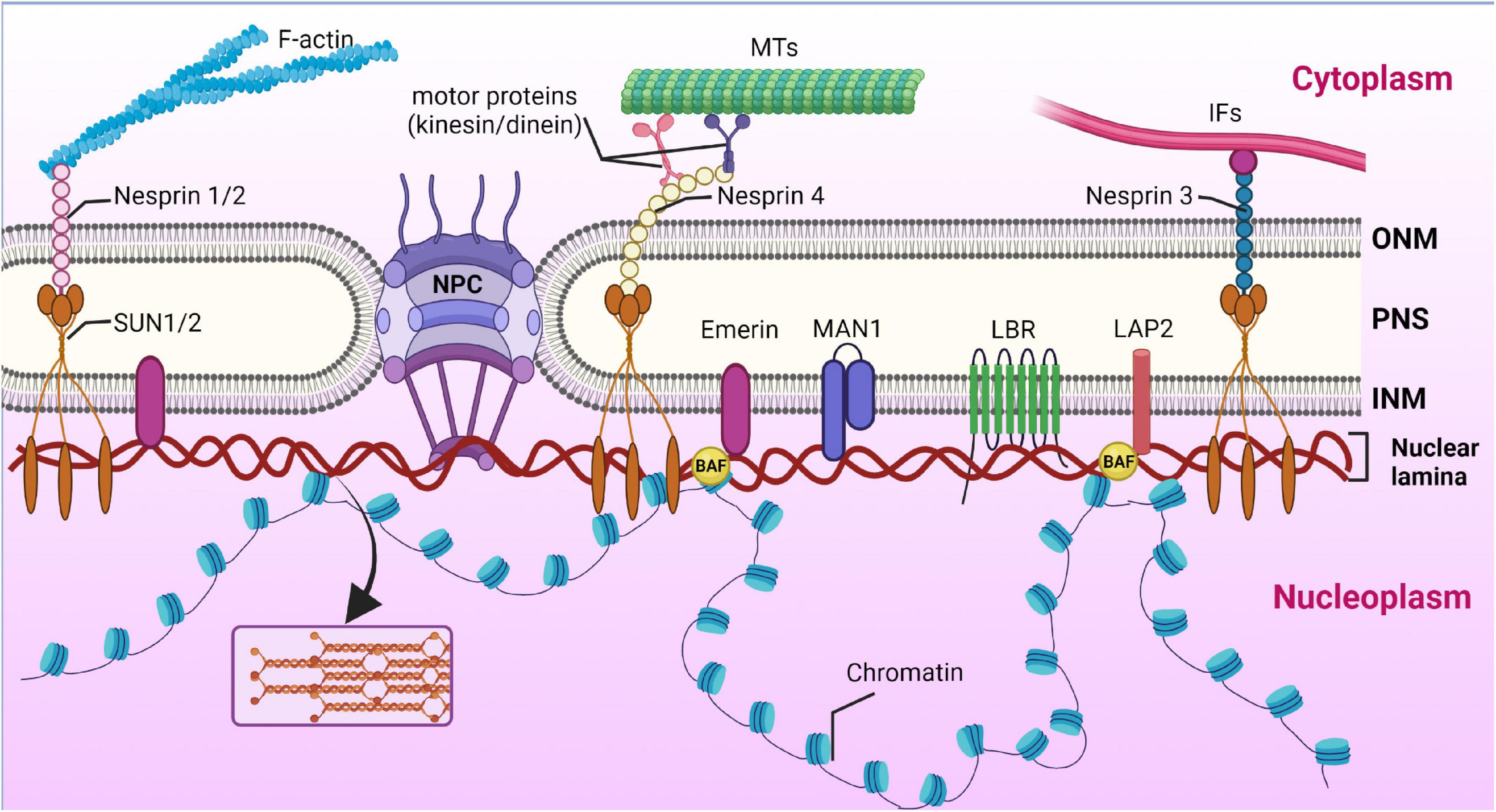
Frontiers | Diversity of Nuclear Lamin A/C Action as a Key to Tissue-Specific Regulation of Cellular Identity in Health and Disease

The prolyl-isomerase PIN1 is essential for nuclear Lamin-B structure and function and protects heterochromatin under mechanical stress - ScienceDirect

Low lamin A levels enhance confined cell migration and metastatic capacity in breast cancer | bioRxiv
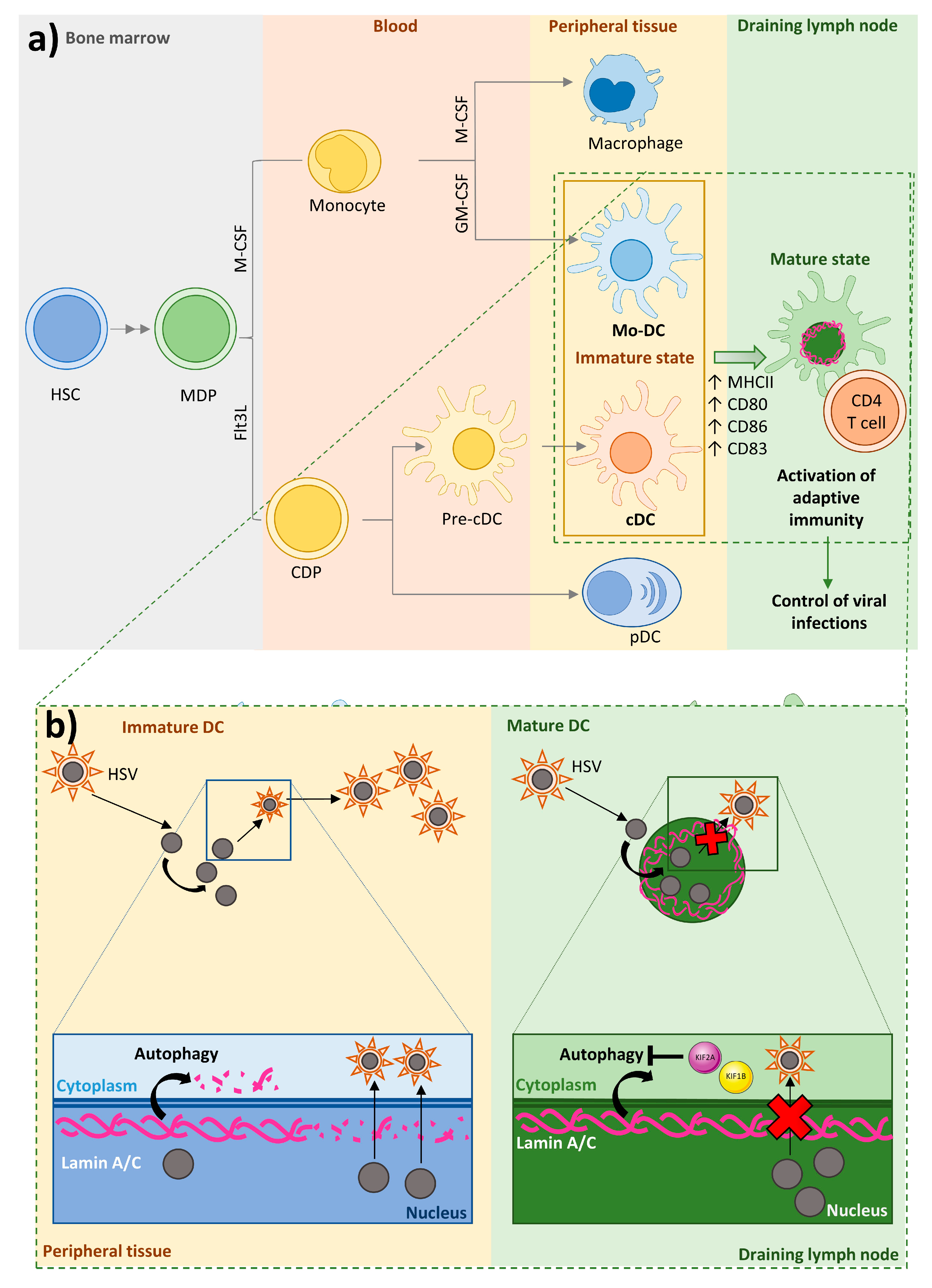
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Lamin A/C and the Immune System: One Intermediate Filament, Many Faces | HTML
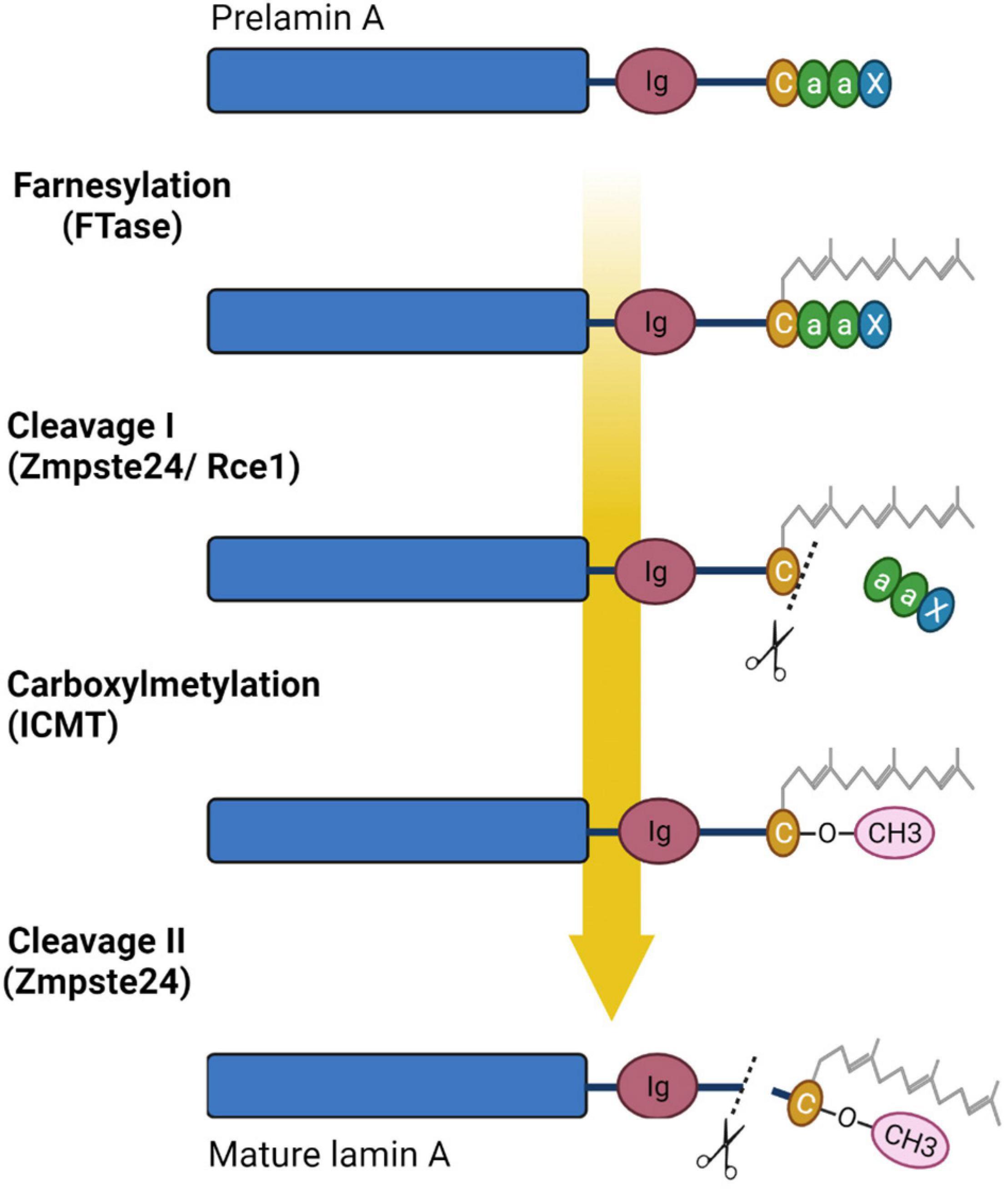
Frontiers | Diversity of Nuclear Lamin A/C Action as a Key to Tissue-Specific Regulation of Cellular Identity in Health and Disease

Degradation of nuclear lamins A/C and B1, LAP2, Nup153, and PARP during... | Download Scientific Diagram

Overexpression of the lamina proteins Lamin and Kugelkern induces specific ultrastructural alterations in the morphology of the nuclear envelope of intestinal stem cells and enterocytes - ScienceDirect
Degradation of nuclear lamins A/C and B1, LAP2, Nup153, and PARP during... | Download Scientific Diagram
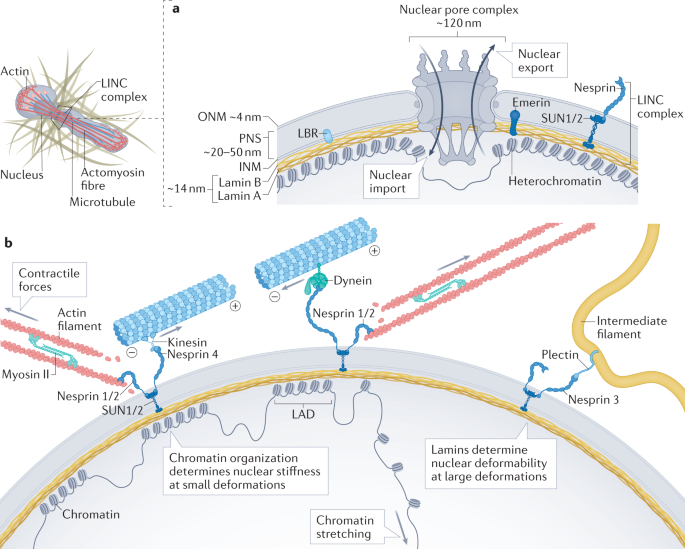
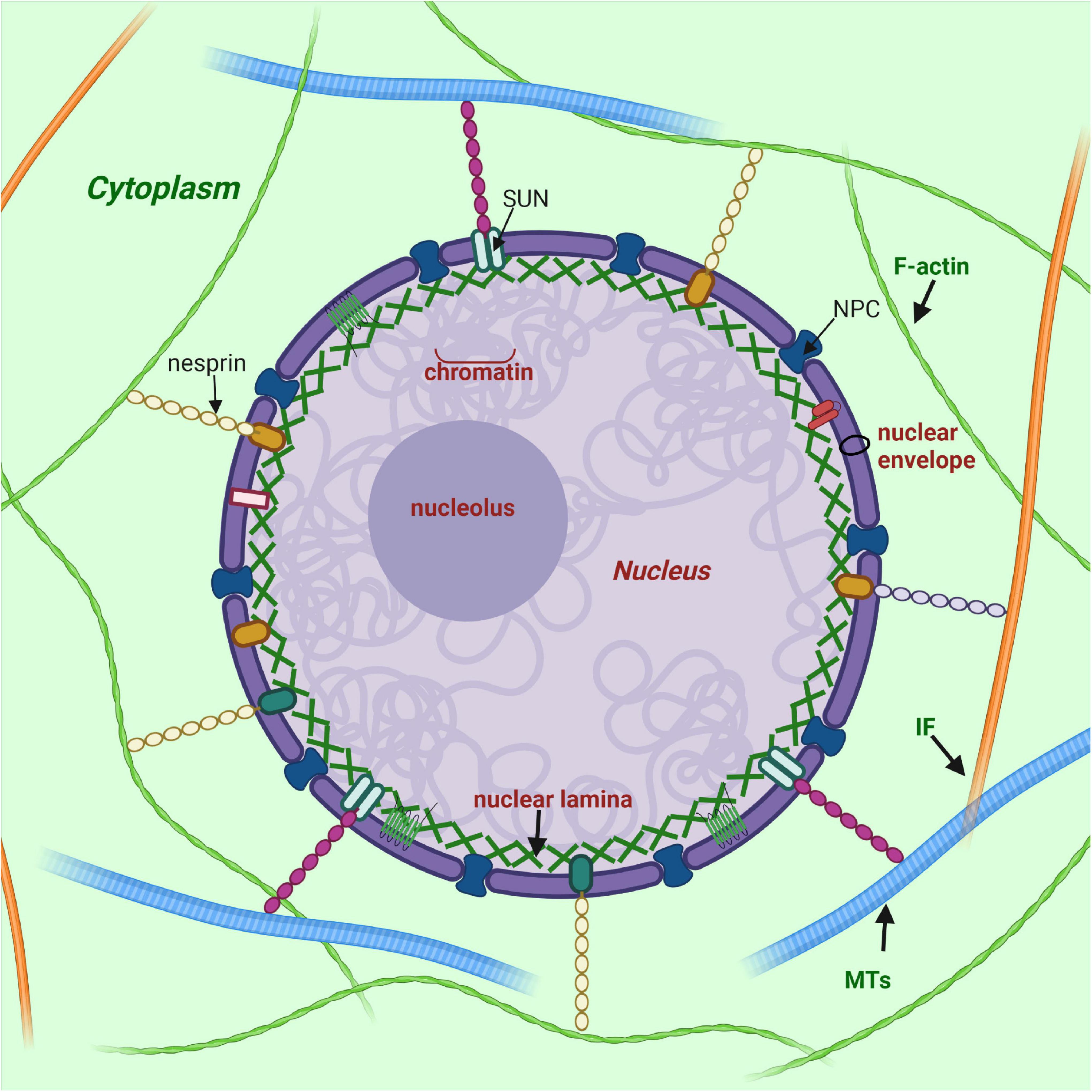
Mechanics and functional consequences of nuclear deformations | Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology